The outbreak of war in Sudan dominated headlines in April, but plenty more has happened in Africa, including in Comoros, Ethiopia, Kenya, Chad, Uganda, Morocco, Cameroon, West Africa, Tanzania and Algeria. African Stream reports.
Related Articles
Related Articles

Art and Activism: Danai Gurira’s Play, “Eclipsed,” Is More Relevant Than Ever
By Lesley Becker
Activism and Art are a potent combination for addressing problems that are both enduring and unendurable. The play, Eclipsed, transports the audience into the intimate dwelling of women struggling to survive while living as sexual slaves in a rebel forces encampment at the end of the Liberian civil war in 2003. The story follows a 15-year-old African girl as she escapes from the encampment to become a child soldier in the rebel forces.
Written by Zimbabwean-American playwright Danai Gurira, Eclipsed made history by being the first Broadway show with an all-female cast, and the first all African-American cast, and an all-female creative team. Eclipsed was on Broadway in 2016, with Oscar winner Lupita Nyong’o in the lead role.
The playwright wants to create awareness about injustices encountered by girls and women around the world by the stories in her plays. “Narrative is in my toolbox, and what I find powerful about narrative is that it actually allows people to be connected, to be disarmed, to see other people across the world that they might perceive of as statistics, [rather than] as actual fellow people that they care about and that they want to see freed to live self-determined lives,” she said in an interview.

Gurira’s work transcends the rationalizations created by terms such as “rape as a weapon of war” that are used to characterize the human experience of sexual violation and violence. Her work portrays the humanity of the captive women, and the difficult choices they must make during a time of war, and how the trauma of those experiences, particularly rape, changes them.
Why is Eclipsed relevant now? In September of 2020, President George Weah of Liberia declared rape a national emergency following a three day protest in the capital city of Monrovia. There were 5,000 anti-rape protesters, and there were violent clashes with authorities. Police tear-gassed thousands of anti-rape protesters. It is difficult to collect meaningful statistics as to the rate of rape in Liberia. A World Health Organization report estimated 75% of women in Liberia at the end of the civil war had experienced rape. That statistic was challenged by American writers because, they wrote, it seems like an improbably high rate. However, the current situation in Liberia, where Covid-19 restrictions have increased the number of Sex and Gender-based attacks by fifty percent, is compared to the same high rate of attacks during the Liberian civil war (1999-2003)
which is the setting of Eclipsed.
The impetus for writing the play came from a 2003 photo appearing in the Western press of Liberian women fighters. Gurira was struck by their attractive appearance, the fierce and intense look in their eyes, and by their guns and their stylish fighting gear. In 2003, the Wall Street Journal interviewed a 20-year-old fighter calle1d Black Diamond, and described her appearance in an almost romantic way: “A pistol and a cellular phone hung from her trendy, wide leather belt. Her jeans were embroidered with roses. Her fellow guerrillas were equally fashionable, wearing tight-fitting jeans, leopard-print blouses and an assortment of jewelry. The number of women in her unit, she said, is a military secret.”

Gurira traveled to Liberia in 2007, setting off on a journey that would reveal that the intensity of the young women fighters in the photo was not empowerment, or a fierce loyalty to the rebel forces and brotherly rebel male fighters. Instead, the style and swagger of the young women covered over the deep trauma of having lived through unspeakable horrors during the civil war including being gang-raped, watching family members murdered, their homes looted and mothers and sisters raped by soldiers. Gurira interviewed thirty women including former women soldiers and women in the Peace Movement who are credited with forcing an end to the Civil War. The characters in the play reflect the histories of those women, as well as Gurira’s research, including the award winning. documentary Pray the Devil Back to Hell and the Human Rights Watch report “Roles and Responsibilities of Child Soldiers”.
Gurira weaves together a story that brings the audience into the women’s lives, using experiences that we can identify within our own lives. The women fuss about their hair, clothing and what will there be for dinner, even as they hide the fifteen-year-old girl from their abuser, the Commanding Officer. The fifteen-year-old, who is called “The Girl,” arrives at the camp as a bright, energetic child, able to read, and having plans to go to school to become a doctor or constitutional lawyer.
The commander, called the “CO” by the women, attacks The Girl when she goes outside to go to the bathroom, then designates her as the “number four” wife. After The Girl is raped by the CO, she returns to the shed where the Wives live together. She is listless and unresponsive to questions from the women about what happened, except to say the CO “did it” to her. Soon after, the CO arrives at the women’s shed, and with dread and anxiety they must line up for him, as he chooses which woman he will take away next.
The women in the play go by their ranking as “Wives,” a system set by the CO, and they do not use each other’s names, but address each other with their number in the ranking. Wife Number One, the eldest wife, was captured when she was twelve, and has been held captive for ten years. Number Two was ousted from the women’s shed and has become a rebel fighter. Number Three is six months pregnant with the CO’s child.
After the CO’s officers loot a village, he gives clothing and other items to Wife Number One, and she finds a book about Bill Clinton. The Girl reads parts of it to some of the other Wives, and their struggle to make sense of Clinton’s troubles provides some comic relief to an otherwise intense and harrowing play.
Wife Number Three calls Monica Lewinsky,“Wife Number Two,” and the woman express wonder at the U.S. Congress trying to remove Clinton as president for having two wives. They remark on the closeness they feel as Liberians to the United States, since it was the United States that set up the founding of their country.

Wife Number Two returns to visit the women’s shed, carrying a large gun and dressed in jeans and a slinky top. She has brought food for the Wives, offering a bag of rice because they have none. Wife Number One has moral authority, and will not accept the food, because Number Two is involved in war atrocities. Number Three, pregnant and bemoaning the shortage of food, wants to accept the rice. The apparent freedom that Number Two has as a soldier appeals to The Girl.
Number Two entices The Girl to become a soldier so that she can get a gun and protect herself from being raped. The Girl follows Number Two and becomes a child soldier. She finds she is required to participate in looting, killing and (much to her dismay) rounding up girls from the ransacked villages to bring to soldiers to be raped.
A woman from the Liberian Woman’s Peace movement secretively visits the Wives to tell them that the war will be ending soon. The unendurable trauma of their war experience has unraveled the Wives’ identities, and they struggle to remember what their names were before the war. Rita, the Peace Woman, coaxes Number One to remember. Finally, she whispers her name, and Rita writes “Helena” in the dirt of the shed floor. The educated and upper-class Peace Woman, Rita, has her own story. Her daughter has disappeared, and she searches the rebel camps in hopes of finding her. Gurira lays bare Rita’s struggle with her classism when Rita airs the complaints of the Peace Women to Helena, saying that the CO is “trying to treat us like we’re village girls they rob from the bush,” without awareness that Helena herself was a 12-year-old girl running from an attack on her family’s home in a village, and captured when she was hiding in the bush.
The play ends when Charles Taylor leaves Liberia, signaling the winding down of the long civil war. The Girl has to choose whether to give up her gun in order to go with the Peace Women group; or to keep her gun and go back to the camp of rebel fighters. Helena (Number One) struggles with her decision to leave at first because her identity is her rank in the camp. Number Two cannot believe that she will be safe if she gives up her gun, and she returns to the rebel fighters’ camp. Number Three has her baby, and she chooses to stay with the C.O., believing that he will take care of her and her baby girl. She named the girl Clintine, after Bill Clinton. The naming of this Liberian child, begotten by rape at a rebel commanders’ camp during wartime, may symbolize Liberia’s call for support from their parent country.
Liberia was founded by the American Colonization Society in the early 1800’s as the first free country in Africa, as part of the “Back to Africa” movement designed by U.S. government to avoid abolishing slavery. For many years, U.S. involvement in Liberia was significant, especially in the exploitation of resources (rubber, diamonds and gold) by the Firestone Tire and Rubber Company starting in the 1920’s. The U.S. supported the violent and repressive government of Samuel Doe (1980-1990) but has been gradually but continuously disengaging since the end of the Cold War. In 1990, at the beginning of the brutal, 14 year Liberian Civil War, the U.S. citizens were evacuated and U.S. involvement, for practical purposes, ended.

The commanders in the Civil War illegally, according to the Geneva Convention, used over 15,000 children under the age of 18 as soldiers in fighting in Liberia between 2000 and 2002. Many people question U.S. disengagement with Liberia, a country considered to be the “stepchild” of the United States. One U.S. expert says that Liberia sees itself as the 51st state. However, while there are significant straightforward needs in Liberia now, such as DNA machines used to determine the perpetrator of a rape and technicians who know how to operate them, there are questions as to why the U.S. has continued to be unresponsive to Liberia’s crisis.
Despite declaring rape to be a national emergency last September, President Weah has not followed through with establishing a special prosecutor for rape, or setting up a national sex offender registry, or establishing Criminal Court E for hearing rape cases across the 15 counties in Liberia. In March of 2021, President Weah unveiled a DNA testing machine to be used to aid prosecution of rape cases. However, media reports indicate that there are no trained technicians who know how to operate the machine in Liberia.
In Our Bodies, Their Battlefields, Christine Lamb writes that rape is the cheapest weapon known to man.” And also one of the oldest, as some scholars analyze the Book of Deuteronomy’s “Law of the Beautiful Captive Woman” to support a view that women may be treated as “spoils of war”. There were many wartime atrocities, but in particular, the weaponizing of raping women and children leaves a lasting imprint on the cultural integrity of a society. The society in Liberia after the war has been called a “culture of impunity” where there is no penalty for attacking women and children.
Danai Gurira founded a website, newsletter and blog called Love Our Girls which raises awareness about girls in African who are abused and forgotten. She writes there:
“As a writer, scripting narratives is my act of resistance, my way of bringing that unheard African female voice front and center and allowing it to manifest its astounding value. I have always had a passion for women and girls, a hope to see them function on the same playing field as men and have the same opportunities and appropriate protections. I want to be more than an actress and storyteller but an advocate for women, not only in underdeveloped countries but all over the world.”

The play’s central theme is that the light inside of each of these women, a light that can be seen clearly in The Girl when she first arrives at the camp, is eclipsed by the trauma of rape and captivity. For the women who become fighters, this is compounded by the horror of the acts of war they witness and participate in.
Eclipsed is about how the light within these women was blocked by the reign of terror of the warlords, their soldiers, and soldiers of the government.
It is an open question as the curtain comes down: what will become of these girls and women when the war has ended? And it is an open question as well: what will it take, locally and globally, to repair the shattered norms that allow rape of children and women to be happening at alarming rates, and to muster the political will to prosecute and convict those who commit those crimes? Gurira uplifts the stories of women and girls in war and invites audiences to see the lives of women and girls who are subjected to repetitive rape, deprivation of food and freedom, by not showing them as “flailing victims” but instead “… these are dynamic women and girls, in the most treacherous of circumstances, and I want the audience to feel at home with them.” The play provokes the empathy that is necessary for social justice.
Lesley Becker is a playwright and director living in Vermont and a Reparative Board member at the Burlington Community Justice Center. Her plays are available to read on New Play Exchange; she is a member of the Dramatist Guild.

Maasai In Tanzania Face Eviction As Government Makes Room for Trophy Hunting

NAIROBI—Close to 500 organizations and 4,747 individuals recently petitioned the Tanzanian government to respect the rights of 70,000 Maasai pastoralists, who are at risk of being evicted from ancestral land because of the government’s collusion with big-game hunting interests.
The petition was delivered after a government official summoned on January 11 village and ward leaders within the 1,500 square kilometers in question, informing them the government would be making a decision for the interest of the country. Maasai residents are calling on President Samia Suluhu Hassan to drop the plans.
“The Maasai residing within the targeted Ngorongoro Conservation Area (NCA) are disallowed from building decent houses or even planting a tree, including even owning a motorbike,” Joseph Oleshangay, a lawyer representing the Maasai, told Toward Freedom. “Successive governments have eternally destined this community to remain impoverished. Now, this current move is a continuation of the abuse meted on the Maasai.”

Royal Intervention
The Tanzanian government had planned to lease the 1,500 square kilometers of Maasai ancestral land to Otterlo Business Corporation (OBC), which a group of Dubai royal families own, according to the petitioners. But after evictions in 2009, 2013 and 2017, the Maasai sought legal recourse. A 2018 East African Court of Justice (EACJ) ruling placed an injunction, prohibiting the destruction of Maasai property, the harassment of the Maasai, and the eviction of the people as well as their more than 200,000 livestock. The injunction remains until the case arrives in court.
Despite several attempts, Tanzania’s Directorate of Presidential Communications declined to respond to Toward Freedom.
According to Oleshangay, with the government ignoring the court, the Maasai community has gone back to a regional court to seek protection and direction.
Within the three years the Maasai people have faced eviction, an estimated 15,000 people have been displaced from their homes.
Isaya Lesion, spokesperson for OBC and himself a Tanzanian national, told Toward Freedom that all the land in Tanzania belonged to the public and the president holds the land in trust of the citizens and may intermittently change its usage for the benefit of the country.
“It has happened before in Ihefu Basin, Mtwara and Kilobero, just to name a few places where evictions by the government have happened to pave the way for development on behalf of the nation.”
Lesion further says that the coterie of Civil Society Organizations (CSO), particularly in Tanzania, who are opposed to the eviction plans have “turned the Maasais into their milking cows, using them to secure funding from external donors. It’s a lucrative business and the key players, who disproportionately live in urban centers, live large as the Maasais continue languishing in poverty.”
However, human rights violations are the crux of the case against the government. Indigenous Maasai pastoralists are recognized as legal inhabitants of the land. About 2 million Maasai roam the arid and semi-arid parts of southern Kenya and northern Tanzania, making them one of the largest pastoral groups worldwide. The Maasai are among the Horn of Africa’s pastoralists and itinerant farmers who have lost access to grazing areas and farmlands because of land grabs.
“Any attempts to evict them will certainly be unlawful, unjust, and discriminatory under national law and the international human-rights obligations and commitments of the Government of Tanzania,” said Ann Henga, executive director of the Dar es Salaam-based Legal and Human Rights Centre (LHRC), in an interview with Toward Freedom.
Competing Interest
Hassan government announced plans to create a wildlife corridor, so OBC could use it for trophy hunting and tourism. The company describes itself on its Twitter account as “Sustainable Utilization (Hunting) and photography outfitters in Tanzania. Investors in Loliondo GCA hunting concession. 100% for wildlife conservation.”
Wildlife is 1 of the crucial aspect in our heritage as a country, we must invest and dedicate more in Anti-poaching and educating more people about the benefits of it. This wasn’t a successful raid b’coz the damage was already done, but it’s progress, consistency must be the key. pic.twitter.com/NjGrvN2gds
— Otterlo Business Corporation (@OBC_Tanzania) December 12, 2017
The government plans to lease to OBC the NCA, which encompasses the Loliondo division, among others. NCA is considered one of the most cinematic landscapes on the globe, with more than 1 million wildebeest migrating through the area every year. It is home to the critically endangered black rhino. In 1979, UNESCO declared the NCA a World Heritage Site.
Joan Carling, co-convener of Indigenous Peoples’ Rights International (IPRI), told Toward Freedom international attention appears to have stamped out eviction efforts.
“The inter-related reasons … are the pressure from UNESCO to address the growing number of humans in the area, which they consider a serious threat to the conservation of wildlife, and, in this sense, would affect the status of the park as a World Wildlife Heritage and Conservation area.”
NCA losing UNESCO recognition would mean fewer tourists. Loliondo is on the main migratory route for wildlife north of the Ngorongoro Crater, east of Serengeti National Park and south of Kenya’s Maasai Mara National Reserve.
In November 2017, the government ended a 25-year-old hunting tourism deal with OBC that reportedly was in exchange for millions of dollars to Tanzania’s armed forces.
The Gulf royal families gave $32,000 to the ruling Chama cha Mapinduzi (CCM) party and $2 million to the Ministry of Natural Resources and Tourism, according to government records The East African newspaper reports to have seen. The monies were given in 1994, according to the regional newspaper, which quotes then-Chief Opposition Chief Whip Tundu Lissu. He said he had interrogated the issue for the past 20 years, but because of the alleged chicanery involved in the deal, the government has kept the details of the engagement shrouded in mystery.
“Once again, the Maasai are facing eviction just to please the UAE royal family, underlining the Tanzanian government insensitivity towards the Indigenous pastoralists, as it clearly prioritizes tourism revenue over its people,” said Dr. Paula Kahumbu, a wildlife conservationist and Chief Executive Officer of Wildlife Direct, a nonprofit registered in both Kenya and the United States, in an interview with Toward Freedom.
Trophy Fees
Despite the November 2017 announcement, OBC did not leave Tanzania for a few days. But current Prime Minister Kassim Majaliwa said OBC would stay. In November 2018, Tanzania lifted a hunting ban, which had been imposed in October 2015 following abuse and misuse of hunting permits. The OBC had been granted an exclusive license to hunt in 1992 during the presidency of Ali Hassan Mwinyi.
The annual hunting license fee is $60,000 per block allocated to a hunting safari company. Trophy fees for hunting an elephant or a lion are the most expensive. It costs $15,000 to kill an elephant and $12,000 to kill a lion. Presently, Tanzania is focused on attracting tourists who can afford a 21-day hunting safari that costs about $60,000, excluding the cost of flights, gun import permits and trophy fees.
“The Maasai have been subjected to a series of human rights violations and violent evictions in the name of conservation and luxury hunting and safari tourism,” Chris Lang of news outlet REDD-Monitor told Toward Freedom. “The rights of Tanzania’s Indigenous peoples and Tanzanian law must come ahead of a deal with a luxury hunting tourism corporation.”
Charles Wachira is a foreign correspondent based in Nairobi, Kenya, and is formerly an East Africa correspondent with Bloomberg. He covers issues including human rights, business, politics and international relations.

AFRICOM Military’s Exercise: The Art of Creating New Pretexts for Propagating U.S. Interests

Phoenix Express 2021 (PE21), a 12-day US-Africa Command (AFRICOM)-sponsored military exercise involving 13 states in the Mediterranean Sea, concluded on Friday, May 28. It had kicked off from the naval base in Tunis, Tunisia, on May 16. The drills in this exercise covered naval maneuvers across the stretch of the Mediterranean Sea, including on the territorial waters of Egypt, Libya, Tunisia, Algeria, Morocco and Mauritania.
The regimes in these countries, which cover the entire northern and northwestern coastline of Africa, participated in the drill – one of the three regional maritime exercises conducted by the US Naval Forces Africa (NAVAF). Belgium, France, Greece, Italy, Malta and Spain were the European states that participated in the drill.
Among the heavyweights deployed in the exercises was the US navy’s USS Hershel “Woody” Williams (ESB 4). The 784-feet-long warship is a mobile military base which “provides for accommodations for up to 250 personnel, a 52,000-square-foot flight deck.. and supports MH-53 and MH-60 helicopters with an option to support MV-22 tilt-rotor aircraft,” according to the Woody Williams Foundation. “The platform has an aviation hangar and flight deck that include four operating spots capable of landing MV-22 and MH-53E equivalent helicopters.”
When the warship entered into its maiden service with the US navy in 2017, Capt. Scot Searles, strategic and theater sealift program manager at the Program Executive Office (PEO) Ships, said, “The delivery of this ship marks an enhancement in the Navy’s forward presence and ability to execute a variety of expeditionary warfare missions.
The Algerian National Navy frigate El Moudamir (F911), Egyptian Navy frigate Toushka (F906) and Royal Moroccan Navy multi-mission frigate Sultan Moulay Ismail (FF 614) were also part of PE21, bringing with them a range weapon systems including surface-to-surface and surface to air missiles, torpedo launchers, heavy naval guns and naval radars.
According to a press release by the US navy, the purpose of this exercise was to test the ability of the participants “to respond to irregular migration and combat illicit trafficking and the movement of illegal goods and materials.”
Smugglers moving goods across the border also illicitly traffic migrants fleeing war or economic crisis in their home countries. AFRICOM has on multiple occasions acknowledged that instability in Libya is the driving force behind the migration crisis.
Who Is Destabilizing the Region?
While ‘Russian intervention’ is blamed for the instability in Libya, AFRICOM played a key military role in the Libyan war in 2012, deposing Muammar Gaddafi, who was a staunch opponent of expanding US military footprint in the region, with the help of radical Islamist organizations. With the exception of Algeria, all the other north African states which participated in PE21 had supported this war in Libya, which has led to mass distress migration.
Many Islamist organizations which emerged amid the anarchy caused by the war were also used by the US and its allies in the Syrian war in a bid to overthrow president Bashar al-Assad, triggering another major wave of destabilization and migration.
Noting that “Syrians.. have (also) entered Libya from neighboring Arab states seeking onward transit to refuge in Europe and beyond,” a US Congressional Research Service report states: “The International Organization for Migration (IOM) reports that nearly 654,000 migrants are in Libya, alongside more than 401,000 internally displaced persons and more than 48,000 refugees and asylum seekers from other countries identified by the United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees (UNHCR).”
The report in 2020 acknowledged that with “human trafficking and migrant smuggling.. trade has all but collapsed compared with the pre-2018 period.”
This migration wave, caused in no small part by AFRICOM-coordinated military interventions in Libya, has since been purported as a reason for further militarization of the region through such exercises as PE21 sponsored by AFRICOM.
The hysteria surrounding migration whipped up by right-wing parties has provided politically fertile ground for the US to mobilize state militaries for such drills. This is despite a fall in undocumented migration.
The need to respond to ‘irregular migration’ with warships is one of the official pretexts which, like the ‘war on terror’, has been used to further the militarization of Africa through AFRICOM since it was established in 2007.
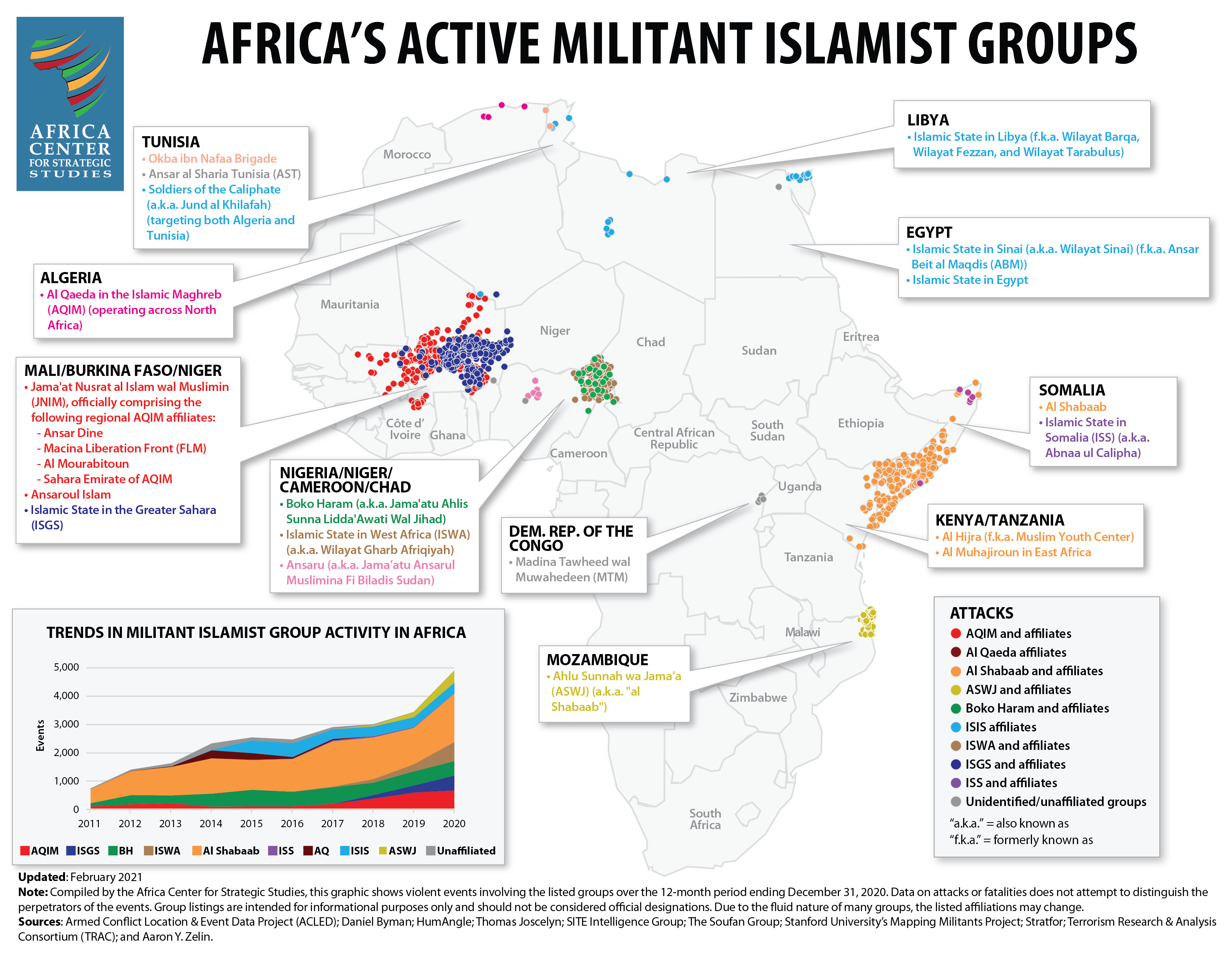
Meanwhile, notwithstanding the fact that the main cause behind the explosion of terrorist organizations in the region was the 2011 Libyan war in which AFRICOM itself was an aggressor, it continues to be portrayed as a bulwark against terrorist organizations. Its operations in Africa over the last decade, including hundreds of drone strikes, correlate with a 500% spike in incidents of violence attributed to Islamist terrorist organizations.
The Chinese Boogeyman
Another justification given by the US for AFRICOM is the perception of a growing Chinese influence. “Chinese are outmaneuvering the U.S. in select countries in Africa,” General Stephen Townsend, commander of AFRICOM, told Associated Press late in April, less than three weeks before the start of PE21.
He went on to claim that the Chinese are “looking for a place where they can rearm and repair warships. That becomes militarily useful in conflict. They’re a long way toward establishing that in Djibouti. Now they’re casting their gaze to the Atlantic coast and wanting to get such a base there.”
Calling out the lack of credibility of this claim, Eric Olander, a veteran journalist and co-founder of The China-Africa Project, wrote: “The Chinese are looking for a base but he doesn’t provide any specifics or any evidence to back up the claim. Again, we’ve heard this before… for years in fact. For all we know the general doesn’t have any more refined intelligence than the same speculation that’s been floating around African social media all these years about a new Chinese base in Namibia or was it Kenya or maybe Angola?”
Townsend also pointed to the Chinese investments in several development projects in Africa. “Port projects, economic endeavors, infrastructure and their agreements and contracts will lead to greater access in the future. They are hedging their bets and making big bets on Africa,” he claimed.
This has been disputed by Deborah Bräutigam, director of the China Africa Research Initiative at Johns Hopkins School of Advanced International Studies, who concluded that China’s economic engagements in Africa are not of a predatory nature.
Bräutigam argues that Chinese economic engagements on the continent are very much in line with the economic interests of these African states, providing jobs to locals and improving public infrastructure.
Neither the concocted threat of Chinese domination of Africa, nor terrorism and irregular migration add up to the raison d’etre of AFRICOM. As former AFRICOM commander Thomas Waldhauser explained to the House Armed Services Committee in 2018, the purpose of AFRICOM is to enable military intervention to propagate “US interests” across the continent, “without creating the optic that U. S. Africa Command is militarizing Africa.” However, the 5,000 US military personnel and 1,000 odd Pentagon employees deployed across a network of 29 bases of AFRICOM in north, east, west and central Africa present a different picture.
AFRICOM has its headquarters in Stuttgart, Germany, which sponsored PE21. While this exercise was still underway, preparations for African Lion 21, Africa’s largest military exercise, had already begun.
This article first appeared in People’s Dispatch.
